LASIK Eye Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
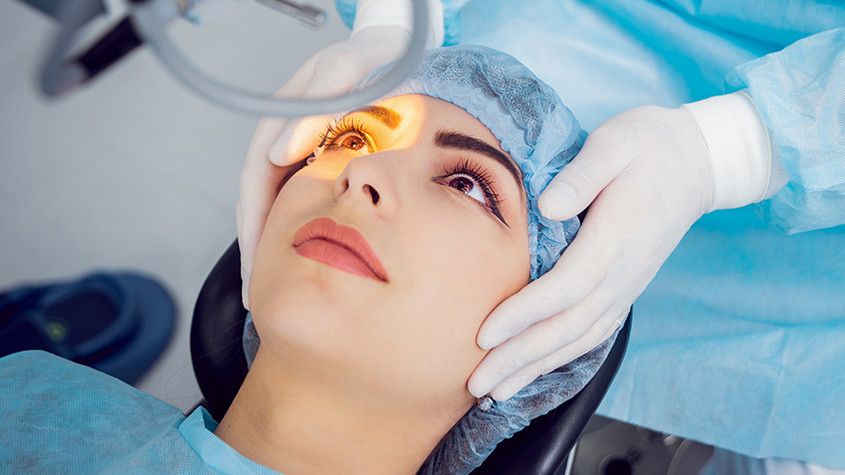
LASIK, or Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis, is a popular and effective refractive surgery procedure that corrects vision problems, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. It uses a laser to reshape the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, so that light entering the eye can be properly focused onto the retina, leading to improved vision.
History of LASIK
LASIK was first developed and performed in the 1990s. Since then, it has undergone significant advancements, making it a safer and more effective procedure. In the early days of LASIK, the procedure was performed using a mechanical microkeratome blade to create a corneal flap. Today, most LASIK procedures are performed using a femtosecond laser, which offers greater precision and reduces the risk of complications.
LASIK Procedure
LASIK is typically performed on an outpatient basis and takes only a few minutes to complete. Before the procedure, the eye is numbed with anesthetic drops, and a lid speculum is used to keep the eyelids open. The surgeon then uses a laser to create a thin flap in the cornea. The flap is then lifted, and the laser is used to reshape the underlying corneal tissue. The flap is then repositioned, and the eye is protected with a patch or shield. The entire procedure is painless and typically only takes a few minutes to complete.
Recovery and Results
After LASIK, most patients experience immediate improvement in their vision, and the majority of patients achieve 20/20 vision or better. However, some patients may experience temporary side effects, such as glare, halos, dry eyes, or fluctuations in vision. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days to a few weeks. Most patients are able to return to their normal activities, including work and driving, within 24 to 48 hours after the procedure.
Benefits of LASIK
LASIK offers several benefits over traditional corrective lenses and glasses. Some of the most significant benefits include:
- Improved vision: LASIK can correct a wide range of vision problems, including nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism, leading to improved vision and reduced dependence on glasses or contacts.
- Convenience: LASIK eliminates the need for glasses or contacts, making it easier to participate in a variety of activities, including sports and other physical activities.
- Cost-effectiveness: Although LASIK is an investment, it can save you money in the long run. The cost of glasses, contacts, and contact lens solutions can add up over time, making LASIK a cost-effective option in the long run.
- Quick recovery: Unlike other types of eye surgery, LASIK typically has a quick recovery time, allowing patients to return to their normal activities within 24 to 48 hours.
- Safety: LASIK has an excellent safety record, with few serious complications. The majority of patients achieve their desired results, and serious complications are rare.
LASIK Candidates
LASIK is not suitable for everyone. Ideal candidates for LASIK include those who:
- Are over 18 years of age
- Have stable vision
- Have no other serious eye problems, such as cataracts or glaucoma
- Have nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism
- Have realistic expectations for the procedure
LASIK Alternatives
If you are not a candidate for LASIK, or if you prefer not to undergo the procedure, there are several alternative treatments available. Some of the most common alternative treatments include:
- Glasses or contacts: Glasses or contacts are the most traditional form of vision correction and can correct a wide range of vision problems, including nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism.
- PRK: PRK, or Photorefractive Keratectomy, is a type of laser eye surgery that is similar to LASIK, but instead of creating a corneal flap, the outer layer of the cornea is removed. PRK is a good option for those who are not suitable candidates for LASIK.
- Implantable contact lenses: Implantable contact lenses, also known as phakic intraocular lenses, are small lenses that are surgically implanted into the eye to correct vision problems. Implantable contact lenses are a good option for those who are not suitable candidates for LASIK or PRK.
- Refractive lens exchange: Refractive lens exchange, also known as clear lens replacement, is a type of cataract surgery that is used to correct vision problems. During the procedure, the clear natural lens of the eye is removed and replaced with an artificial lens to correct vision problems.
To Sum It Up
LASIK is a safe, effective, and convenient way to correct a wide range of vision problems, including nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. The procedure is quick, has a short recovery time, and offers long-lasting results. If you are considering LASIK, it is important to talk to your eye doctor to determine if you are a good candidate for the procedure and to learn more about the benefits and risks involved. With the right information and guidance, you can make an informed decision about whether LASIK is the right choice for you.
DISCLAIMER: THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images, and other material contained on this website is for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.